How Cookies are Worked
A website sends a cookie to your browser, which stores it locally. On subsequent visits, the browser sends the cookie back to the website’s server, enabling the site to remember your preferences, logins, and browsing history. This functionality improves navigation and personalizes the user experience
Enhancing User Experience and Driving Business Success"
- Session Management: Keep you logged in and remember actions like adding items to a cart.
- Personalization: Tailor the user experience based on preferences or history.
- Analytics: Track user behavior and site performance.
- Advertising: Deliver targeted ads and measure marketing effectiveness.
- Security: Enhance site protection and secure user data.
Positive Aspects:
Enhanced User Experience:
- Remembering preferences (e.g., language or theme).
- Maintaining login sessions for convenience.
Personalization:
- Tailoring content, recommendations, and ads to user interests.
Efficiency:
- Speeding up website interactions by storing data locally.
- Reducing the need to re-enter information (e.g., autofill forms).
Analytics and Insights:
- Helping website owners understand user behavior for improvements.
- Identifying and resolving technical issues efficiently.
- Keeping track of cart items and wish lists.
- Enabling personalized promotions and offers.
Security:
- Enhancing protection by validating user sessions.
Detecting suspicious or unauthorized activity.
Negative Aspects:
Privacy Concerns:
- Tracking user behavior without explicit consent, especially via third-party cookies.
- Potential misuse of data for intrusive advertising or profiling.
Security Risks:
- Cookies can be intercepted or exploited by attackers (e.g., cross-site scripting or session hijacking).
- Stolen cookies may expose sensitive information, like login credentials.
Over-Reliance on Consent:
- Excessive cookie consent pop-ups can frustrate users.
- Many users unknowingly accept cookies without understanding their implications.
Data Overload:
- Too many cookies can slow down browser performance.
- Some cookies persist for long durations, unnecessarily occupying storage.
Manipulation of User Behavior:
- Targeted ads based on cookie data may manipulate purchasing decisions.
- Over-personalization can limit exposure to diverse content.
Regulation Challenges:
- Mismanagement of cookies can lead to violations of laws like GDPR or CCPA, affecting both users and businesses.
Purpose of Using Cookies by Website Owners
Cookies are essential tools for website owners to enhance user experience, streamline operations, and achieve business goals. Here’s how cookies benefit website owners:
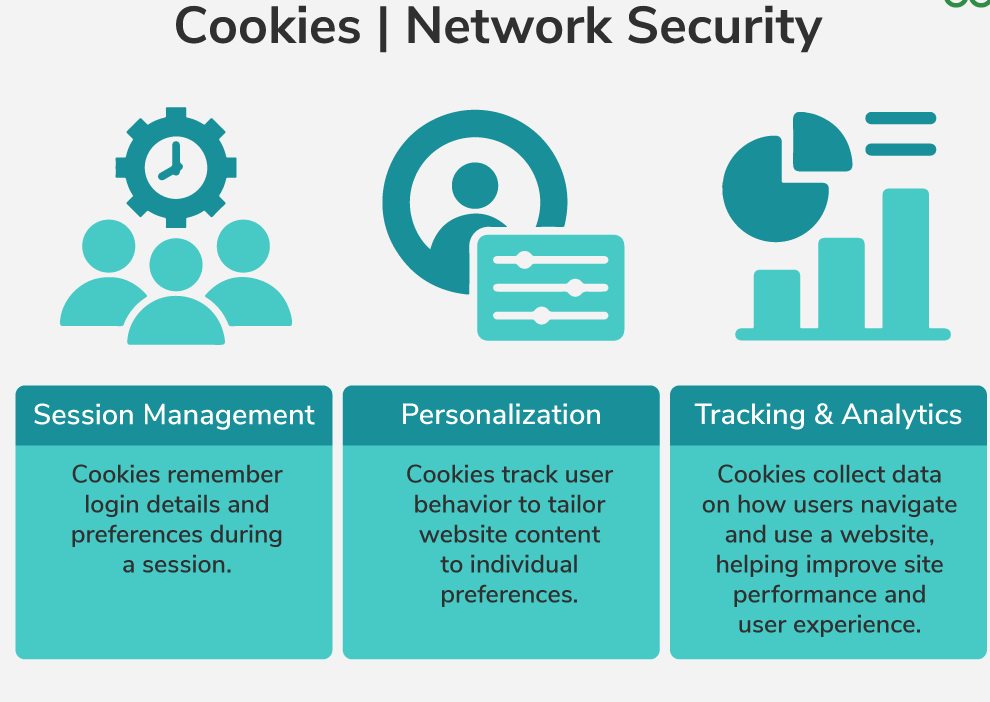
Session Management: Cookies store login information to keep users logged in as they navigate between pages.
- Example: Keeping a user logged in on an e-commerce site.
Personalization: Cookies remember preferences, language, or theme settings for a customized user experience.
- Example: A website remembering your language choice or theme (light/dark).
Tracking & Analytics: Cookies help websites track user behavior for analytics and improve site performance.
- Example: Google Analytics uses cookies to monitor how users interact with a website.
Advertising: Cookies are used to display targeted ads based on user behavior and interests.
- Example: Ads related to products you’ve recently searched for.

